Table of Contents
Introduction: Market Analysis – When the Market Screams, Listen Carefully
In today’s business landscape, chaos isn’t just an occasional visitor—it’s practically a permanent resident. Markets fluctuate wildly, consumer preferences evolve at lightning speed, and technological disruptions rewrite industry rules overnight. This persistent turbulence creates a deafening noise that many organizations struggle to interpret, leading to reactive rather than proactive strategies.

Market analysis emerges as the essential translator in this environment of constant change. More than just a tool for reducing confusion, properly conducted market analysis transforms apparent disorder into strategic opportunity. It acts as a noise-canceling mechanism that helps businesses hear the meaningful signals amid the market’s screams.
At its core, market analysis serves as the intelligence nerve center that connects various business functions. While traditionally associated with marketing departments, its reach extends throughout the organization. For corporate strategy teams, market analysis provides the foundation for sustainable competitive advantage. Customer service departments leverage these insights to anticipate needs and enhance satisfaction. Information technology relies on market intelligence to prioritize digital investments that align with consumer expectations. Operations teams use market analysis to optimize supply chains and production schedules based on projected demand patterns.
This interconnected nature of market analysis explains why it has evolved from a specialized marketing function to a cross-disciplinary approach that informs decision-making at all levels. The organizations that thrive amid chaos aren’t necessarily the largest or most resource-rich—they’re the ones that develop superior capabilities in capturing, interpreting, and acting upon market intelligence.
| Relationship Between Market Analysis and Business Functions |
|---|
| Corporate Strategy: Uses market analysis to identify growth opportunities, assess competitive threats, and make resource allocation decisions |
| Marketing: Employs market analysis to develop targeted campaigns, optimize channel selection, and refine messaging |
| Sales: Utilizes market insights to prioritize prospects, anticipate objections, and tailor value propositions |
| Product Development: Relies on market analysis to identify unmet needs, validate concepts, and prioritize features |
| Customer Service: Leverages market understanding to anticipate support requirements and improve experience design |
| Information Technology: Uses market forecasts to develop technology roadmaps aligned with emerging consumer behaviors |
| Operations: Applies market intelligence to optimize supply chains, production scheduling, and capacity planning |
This article explores six transformative powers of market analysis that can bring order to chaos—abilities that turn market complexity from a liability into an asset. These approaches aren’t merely tactical responses to uncertainty; they represent strategic capabilities that allow organizations to navigate turbulence with confidence and purpose.
1. Mapping the Mayhem: How Market Analysis Reveals Focus
In chaotic markets, the temptation to cast the widest possible net becomes nearly irresistible. Many businesses fall into the trap of pursuing everyone, spreading resources thinly across diverse customer groups with divergent needs. This approach typically results in generic offerings that resonate deeply with no one.
Market segmentation analysis cuts through this confusion by identifying distinct customer groups with similar needs, behaviors, or characteristics. Rather than viewing the market as an undifferentiated mass, segmentation reveals the underlying structure and logic. This analytical approach transforms overwhelming complexity into manageable clusters where focused strategy becomes possible.
The power of segmentation lies not just in identifying groups but in revealing which segments represent the greatest strategic opportunity. By analyzing segment size, growth potential, competitive intensity, and alignment with organizational capabilities, businesses can direct resources where they’ll generate maximum return. This focused approach stands in stark contrast to the scattered efforts that characterize many organizations’ responses to market chaos.
Consider how Lululemon transformed the athletic apparel market through strategic segmentation. Rather than competing directly with industry giants like Nike and Adidas across all customer groups, they focused intensely on yoga practitioners—a segment underserved by existing players. This segmentation-driven strategy allowed Lululemon to develop deep expertise in this community’s needs, resulting in products and experiences tailored specifically to their preferences. From this focused starting point, they gradually expanded into adjacent segments while maintaining their distinctive approach.
Effective segmentation also provides clarity regarding which customers not to pursue. This disciplined exclusion may seem counterintuitive during turbulent times when any revenue appears attractive, but it prevents the dilution of resources that undermines competitive advantage.
| Key Benefits of Strategic Market Segmentation |
|---|
| Resource Optimization: Concentrates limited resources on the highest-potential opportunities rather than dispersing efforts across too many fronts |
| Message Resonance: Enables development of marketing communications that speak directly to specific customer pain points and aspirations |
| Product Differentiation: Facilitates the creation of offerings tailored to segment-specific needs rather than one-size-fits-all solutions |
| Pricing Precision: Allows for segment-appropriate pricing strategies based on distinct value perceptions and willingness to pay |
| Channel Alignment: Guides selection of distribution channels that align with segment shopping preferences and behaviors |
| Competitive Insulation: Creates defensible market positions based on deep segment expertise that generalists struggle to match |
| Innovation Focus: Directs product development resources toward solving specific problems for defined customer groups |
The discipline of regular segmentation analysis proves particularly valuable during market disruptions when customer behaviors and preferences undergo rapid shifts. Organizations that continuously refresh their segmentation models gain early visibility into emerging opportunities that competitors miss amid the noise.
2. Seeing the Invisible: Trendspotting in Economic Uncertainty

During periods of economic uncertainty, most organizations fixate on immediate threats—cutting costs, preserving cash flow, and maintaining current customer relationships. While these reactions are understandable, they often blind businesses to the emerging trends that will shape future competitive dynamics. Market analysis provides the perceptual tools to detect weak signals of change before they become obvious to everyone.
Trendspotting through systematic market analysis involves looking beyond the immediate chaos to identify patterns that suggest directional shifts in customer behavior, technological adoption, or regulatory environments. These early indicators often appear first at the margins before spreading to the mainstream—making them easy to dismiss amid more pressing concerns.
Early detection of trends provides significant competitive benefits. It broadens the timeframe for strategic action, enabling organizations to align themselves proactively with market changes instead of hastily trying to adapt. While competitors may be immobilized by uncertainty, organizations that are attuned to trends can take decisive actions grounded in well-informed forecasts regarding market directions.
Consider how Zoom identified and acted upon the trend toward remote work long before the pandemic accelerated this shift. Their market analysis detected growing demand for simplified video conferencing solutions at a time when most providers were focused on complex enterprise systems. This early trend recognition allowed Zoom to develop and refine their offering while competitors remained focused on traditional markets, positioning them perfectly to capitalize when remote work suddenly became universal.
Effective trendspotting requires both quantitative and qualitative approaches. Quantitative analysis identifies statistical patterns and correlations that may indicate emerging shifts, while qualitative techniques like ethnographic research provide deeper understanding of the underlying motivations and contexts driving those changes.
| Essential Trendspotting Techniques in Market Analysis |
|---|
| Leading Indicator Monitoring: Tracking early warning signals that typically precede major market shifts |
| Fringe Consumer Analysis: Studying early adopters and outlier behaviors that often prefigure mainstream trends |
| Cross-Industry Pattern Recognition: Identifying trends that have transformed adjacent industries and may transfer to your sector |
| Social Listening: Analyzing unstructured data from social platforms to detect emerging conversations and concerns |
| Scenario Planning: Developing multiple future scenarios based on identified trend vectors to prepare for various outcomes |
| Technology Diffusion Tracking: Monitoring the adoption curves of technologies that could disrupt existing market structures |
| Regulatory Horizon Scanning: Anticipating policy and regulatory shifts that will reshape market conditions |
Organizations with superior trendspotting capabilities transform economic uncertainty from a threat into an opportunity. While competitors are consumed with navigating present chaos, these firms are quietly positioning themselves for the emerging future—investing ahead of obvious market shifts and building capabilities that will be at a premium when trends materialize.
3. The Competitor Compass: Using Market Analysis for Strategic Direction
In chaotic marketplaces, understanding competitive dynamics becomes simultaneously more challenging and more critical. Disruptions create openings for new entrants, encourage established players to invade adjacent territories, and render traditional competitive barriers increasingly permeable. Without a sophisticated understanding of this shifting competitive landscape, strategic decisions become little more than guesswork.
Market analysis functions as a compass in this competitive fog, providing clear directional signals when visibility is limited. Rather than reacting to competitor moves in isolation, comprehensive competitive intelligence reveals the underlying logic guiding rival strategies. This deeper understanding allows organizations to anticipate competitive threats before they materialize and identify uncontested spaces where growth is possible without direct confrontation.
The Japanese market offers a compelling example of how competitive analysis shapes strategic direction. Toyota’s systematic analysis of competitive market positioning in the American automotive market revealed an unoccupied position between mass-market and luxury vehicles. This insight led to the creation of the Lexus brand, which established a new competitive category that existing American and European manufacturers were slow to address.
In the European context, Spotify’s market analysis identified a critical weakness in Apple’s music strategy—the requirement to purchase entire albums rather than individual tracks. This competitive insight informed Spotify’s subscription-based streaming model, which addressed consumer frustration with existing offerings and created a sustainable competitive advantage.
Sophisticated competitive analysis extends beyond tracking obvious rivals to mapping the entire competitive ecosystem, including potential entrants from adjacent industries. This broader perspective helps organizations identify threats that might otherwise remain invisible until they’ve gained significant momentum.
| Dimensions of Effective Competitive Analysis |
|---|
| Strategic Intent Assessment: Looking beyond current offerings to understand competitors’ long-term strategic objectives and directional focus |
| Capability Mapping: Evaluating competitors’ organizational strengths, weaknesses, and distinctive competencies that shape their strategic options |
| Resource Allocation Analysis: Tracking where competitors are investing resources as an indicator of future strategic priorities |
| Partnership Ecosystem Monitoring: Identifying alliance networks and strategic relationships that extend competitive reach and capabilities |
| Innovation Pipeline Tracking: Monitoring patent filings, R&D investments, and talent acquisition patterns that signal future product directions |
| Pricing Strategy Analysis: Examining competitors’ pricing approaches to understand their value positioning and target customer segments |
| Organizational Culture Assessment: Evaluating how competitors’ cultural attributes influence their ability to execute various strategies |
The most valuable competitive insights often come from synthesizing information across multiple domains rather than from any single data point. By connecting patterns in hiring, partnerships, investments, and messaging, market analysis reveals competitors’ true strategic direction despite the fog of market chaos.
4. Pricing in the Storm: Value Perception Through Market Insight
During economic turbulence, pricing decisions become extraordinarily challenging. Cost pressures mount, customer price sensitivity increases, and traditional pricing benchmarks lose reliability. Many organizations respond by retreating to cost-plus formulas or matching competitor moves—approaches that frequently destroy value and undermine long-term market position.
Market analysis provides an alternative foundation for pricing strategies grounded in customer value perception rather than internal costs or competitive reference points. This approach recognizes that customers don’t buy based on what products cost to produce but on the value they expect to receive. During chaotic periods, this value-based orientation proves particularly critical as it maintains pricing integrity even as market conditions fluctuate wildly.
The American economy offers numerous examples of companies that have leveraged market analysis to maintain value-based pricing even during economic downturns. Apple’s consistent premium pricing strategy through multiple recessions reflects their deep understanding of how their customers perceive value—prioritizing ecosystem integration, design aesthetics, and brand prestige over absolute price points.
Similarly, in the Indian market, Tata Group’s detailed analysis of value perception across different economic segments has enabled them to maintain price integrity even during periods of inflation and economic uncertainty. Their “more for less” value proposition in categories like automotive and hospitality reflects market insights about Indian consumers’ particular definition of value.
Effective value-based pricing requires continuous feedback loops that capture evolving customer perceptions. These mechanisms provide early warning when value alignments shift, allowing pricing adjustments before revenue or market share erosion becomes significant.
| Key Elements of Value-Based Pricing Through Market Analysis |
|---|
| Value Driver Identification: Determining which product/service attributes create the most significant value for different customer segments |
| Willingness-to-Pay Research: Using advanced research techniques to quantify how much customers will pay for specific benefits and features |
| Price Sensitivity Mapping: Measuring how price elasticity varies across segments, purchase occasions, and product categories |
| Value Communication Testing: Evaluating how different messaging approaches influence value perception and price acceptance |
| Pricing Architecture Design: Developing tiered offerings that align with value perception variations across customer segments |
| Competitive Price Positioning: Strategically positioning prices relative to competitors based on comparative value delivery |
| Economic Impact Modeling: Projecting how different pricing scenarios will affect revenue, margin, and market share |
Organizations with sophisticated pricing capabilities derived from market analysis avoid the pricing chaos that typically accompanies market disruption. Rather than engaging in destructive price wars or making panic-driven discounting decisions, they maintain pricing discipline informed by deep customer understanding—preserving margins while competitors sacrifice profitability in response to temporary market pressures.
5. Demand Without Doubt: Forecasting with Agility and Precision
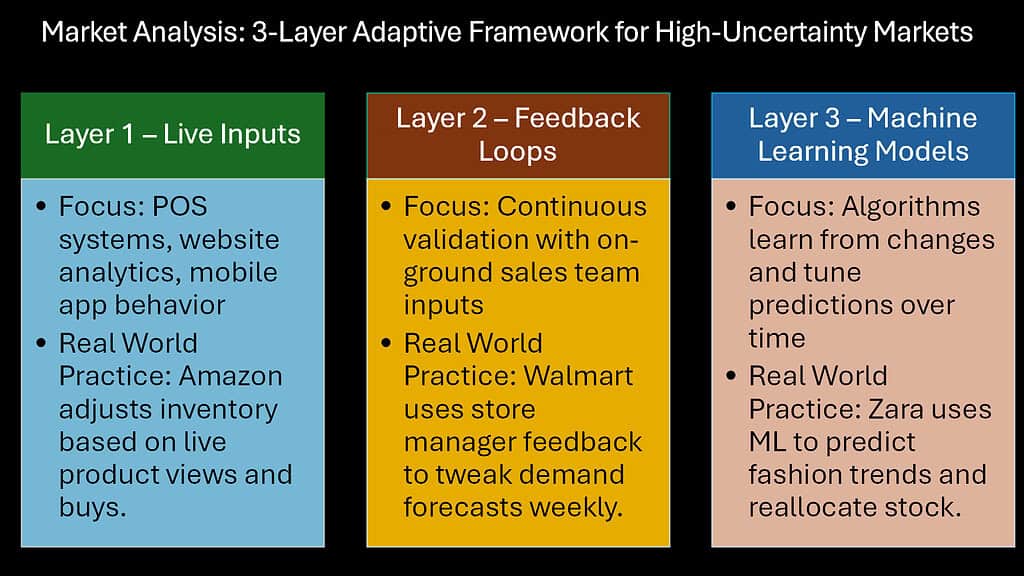
Traditional demand forecasting approaches often collapse during periods of market turbulence. Historical patterns lose predictive value, established correlations break down, and familiar cyclical rhythms become unreliable. The resulting forecast uncertainty ripples throughout organizations, compromising inventory decisions, production scheduling, staffing levels, and financial planning.
Advanced market analysis enables a more resilient approach to demand forecasting that maintains reasonable accuracy even amid unprecedented conditions. Rather than relying exclusively on historical extrapolation, these methods incorporate real-time market signals, scenario-based planning, and rapid feedback loops that continuously refine projections as new information emerges.
The Japanese manufacturing sector exemplifies this sophisticated approach to demand forecasting. Companies like Toyota have pioneered systems that combine traditional statistical methods with rapid-response market sensing capabilities. Their approach recognizes that forecast accuracy depends less on mathematical complexity and more on the speed with which new information can be incorporated into projections.
European retailers like Zara have similarly developed forecasting capabilities that detect and respond to demand shifts in near real-time. Their market analysis systems capture early sales patterns for new merchandise and rapidly adjust production plans before committing to full inventory positions. This approach has proven particularly valuable during fashion seasons disrupted by economic uncertainty or unexpected events.
The most effective forecasting methodologies acknowledge uncertainty explicitly rather than pretending to eliminate it. They produce ranges of likely outcomes with associated probabilities rather than single-point predictions, giving decision-makers a more realistic understanding of potential scenarios.
| Advanced Demand Forecasting Techniques |
|---|
| Signal Detection Systems: Algorithms that identify early indicators of demand shifts from multiple data sources |
| Dynamic Baseline Adjustments: Methods for rapidly revising baseline forecasts when established patterns break down |
| Probabilistic Scenario Modeling: Techniques that generate forecast ranges with confidence intervals rather than point estimates |
| Contextual Data Integration: Approaches that incorporate non-traditional variables (social sentiment, weather patterns, etc.) into forecasting models |
| Cross-Functional Input Processes: Structured methods for capturing qualitative insights from sales, marketing, and other customer-facing functions |
| Rapid Learning Algorithms: Machine learning systems that continuously improve forecast accuracy by learning from prediction errors |
| Demand Segmentation: Techniques that develop separate forecasts for different demand patterns rather than aggregating dissimilar behaviors |
Organizations with superior demand forecasting capabilities navigate chaotic markets with significantly less inventory risk, capacity mismatch, and resource waste than competitors relying on traditional approaches. This capability becomes particularly valuable during supply chain disruptions when production and procurement decisions must be made despite heightened uncertainty.
6. Rewriting the Playbook: Innovation Backed by Market Analysis
During market upheaval, many organizations instinctively retrench—focusing on protecting core business rather than pursuing innovation. This defensive posture seems prudent but often concedes the future to more aggressive competitors who recognize that disruption creates unique opportunities for business model reinvention and market creation.
Market analysis provides the confidence to innovate amid chaos by grounding creative thinking in robust customer understanding. Rather than innovation driven by internal perspectives or technological possibilities alone, market-informed innovation addresses genuine needs that emerge or intensify during turbulent periods.
The USA economy demonstrates this principle through companies like Netflix, which has repeatedly used market analysis to guide transformative innovations. Their transition from DVD rental to streaming and later to original content production was driven not by technological capability alone but by deep analysis of evolving entertainment consumption patterns and unmet viewer needs.
Similarly, in European economies, companies like Spotify have leveraged market analysis to continuously refine their innovation approach. Their development of curated playlists, algorithmic recommendations, and podcast integration all stemmed from systematic analysis of listening behaviors and friction points in the music consumption experience.
The most powerful innovation insights often emerge at the intersection of multiple data sources—combining quantitative market measurements with qualitative understanding of customer contexts and pain points. This integration reveals innovation opportunities that remain invisible when viewed through any single analytical lens.
| Market-Driven Innovation Approaches |
|---|
| Jobs-to-Be-Done Analysis: Identifying the fundamental tasks customers are trying to accomplish rather than focusing on current solution characteristics |
| Friction Mapping: Systematically documenting pain points in current customer experiences to identify innovation opportunities |
| Value Migration Tracking: Monitoring how economic value shifts across industry value chains to identify emerging profit pools |
| Non-Customer Research: Studying individuals who don’t currently use category offerings to understand barriers and unmet needs |
| Parallel Industry Analysis: Identifying successful innovations in adjacent industries that could be adapted to current markets |
| Lead User Methodology: Engaging with sophisticated customers who are already attempting to solve problems ahead of mainstream markets |
| Minimum Viable Concept Testing: Rapid experimentation with simplified versions of innovation concepts to validate market response |
Organizations that maintain aggressive innovation programs backed by robust market analysis emerge from periods of market chaos in substantially stronger competitive positions. While rivals focus exclusively on weathering the storm, these companies are simultaneously building the capabilities and offerings that will define the next market era.
Conclusion: From Noise to Navigation—Why Market Analysis Isn’t Optional
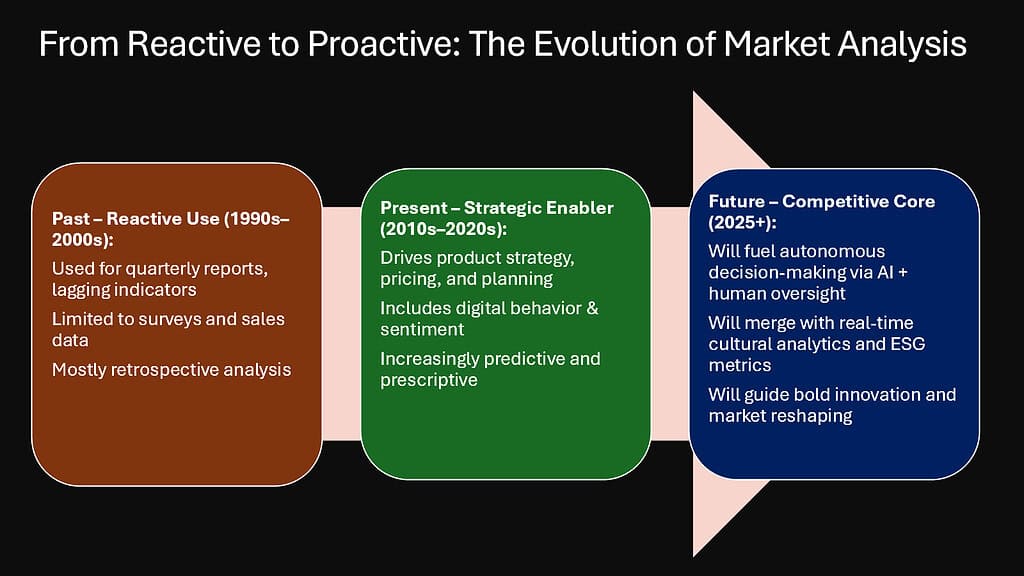
In chaotic business environments, market analysis transforms from a periodic supporting function into an essential navigational system. The organizations that thrive amid turbulence are invariably those with superior capabilities for sensing, interpreting, and acting upon market intelligence—converting overwhelming complexity into strategic clarity.
The six approaches explored in this article—strategic segmentation, trendspotting, competitive analysis, value-based pricing, agile forecasting, and market-driven innovation—represent complementary dimensions of this navigational capability. Together, they form a robust system for extracting meaning from market chaos and converting apparent disorder into strategic opportunity.
Establishing these capabilities necessitates more than sporadic market research initiatives or external analyses. It calls for the cultivation of a comprehensive market orientation throughout the organization—a collective dedication to comprehending and addressing customer needs that influences every function and level. This orientation integrates formal analytical methods with cultural aspects that emphasize an external viewpoint rather than relying on internal assumptions.
The implementation challenge lies not primarily in technical complexity but in overcoming organizational resistance to externally derived insights that challenge established beliefs. Market analysis frequently produces conclusions that contradict executive intuition or threaten existing power structures—creating friction that must be managed through leadership commitment and cultural reinforcement.
| Building Sustainable Market Analysis Capabilities |
|---|
| Cross-Functional Integration: Creating structural connections that ensure market insights flow to all decision centers |
| Insight Activation Systems: Developing processes that convert analysis into specific action plans with clear accountability |
| Analytical Talent Development: Building specialized skills in both technical analysis and insight interpretation |
| Knowledge Management Infrastructure: Implementing systems that capture and distribute market intelligence throughout the organization |
| Decision Process Integration: Embedding market analysis requirements into formal strategic and operational decision protocols |
| Analytical Tool Investment: Deploying technologies that enhance the organization’s ability to process complex market data |
| Performance Measurement Alignment: Creating metrics and incentives that reward market-responsive behaviors |
The market analysis capabilities described throughout this article represent more than tactical responses to temporary uncertainty—they constitute strategic assets that deliver sustainable competitive advantage. In environments characterized by continuous disruption rather than occasional turbulence, these capabilities have shifted from optional enhancements to core survival requirements.
Organizations that invest systematically in market analysis capabilities don’t just survive chaos—they actively harness its energy to accelerate past competitors still struggling to make sense of the noise. When markets scream, these organizations don’t just listen carefully—they understand the message and act decisively while others remain paralyzed by confusion.




