Table of Contents
Discoveries by JWST (James Webb Space Telescope)
Launched on 25th December 2021, JWST (James Webb Space Telescope) is supposed to be a gift to the scientific community. However, within a few months of its launch, it became a gift to humanity. The discoveries by JWST (James Webb Space Telescope) had a profound implication not just for science and the scientific community, but for the entire humanity. The discoveries by JWST have altered the way we look at our Universe, Solar System, our neighboring planets, and even our existence.
The telescope was hailed as the Next Generation Space Telescope. It is supposed to be the successor to the revered Hubble Space Telescope. JWST is also supposed to carry on the work of Kepler Space Telescope which is to find habitable, rocky, and Earth-like exoplanets outside our own solar system. The discoveries by JWST have shown the existing discoveries by its predecessors in new light and even unlocked a deeper understanding of those discoveries.
Compared to Hubble, JWST is much bigger in size and equipped with high-resolution and sensitive instruments. JWST has 18 mirrors which are made of gold-plated beryllium. Together it gives JWST’s mirror a diameter of 21.32 feet. Due to this, JWST is able to capture 0.6 to 28-micron wavelengths of light which ranges from long wavelength visible red light to medium wavelength infrared light. In order to be able to see the infrared light, JWST is being stationed far away from Earth so that it can be kept extremely cold. This ensures that the telescope does not capture its own infrared light.
Due to these above features, the qualities of the discoveries by JWST will surpass Hubble’s discoveries. We know that after the Big Bang, the Universe is expanding and the galaxies are moving away from each other. For this, the lights emitted by faraway galaxies have turned into infrared. Hubble is not sensitive enough to capture this infrared wavelength. But, as JWST is capable of observing the infrared wavelength, it can peer deep into the Universe and unveil the aspects that even Hubble could not see through.
With that prelude, let’s look into the top 10 incredible discoveries by JWST.
1. New View of Hubble’s Ultra Deep Field
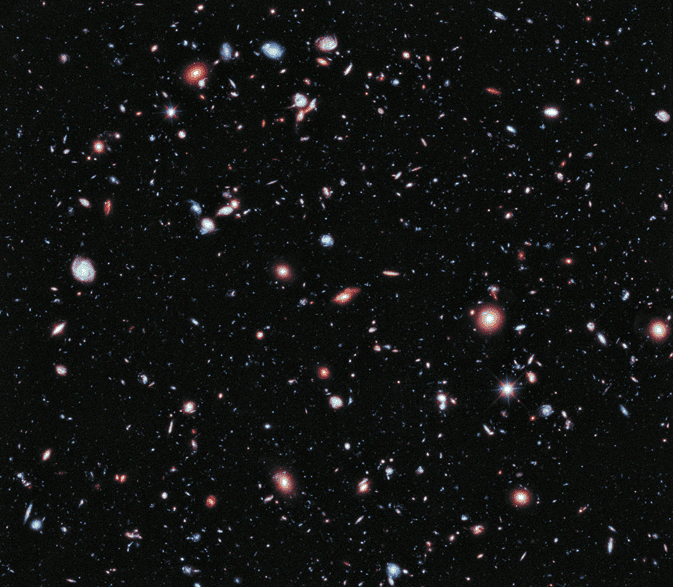


One of the first discoveries by JWST dethroned one of the greatest discoveries made by its predecessor. In 2003, the Hubble Telescope looked at a section of space called ‘Fornax’ and clicked an amazing image of the Universe which became famous as ‘Farthest Ever View of the Universe’. This image contained young galaxies which were formed just 800 million years after the Big Bang. At that point in time it was the furthest the human kind had ever seen.
But that changed after the JWST came into action. It was not even a year since JWST was launched and it took a picture at the galaxy cluster SMACS 0723. The mass of the galaxy cluster has put enormous gravitational force on the space around the cluster. As a result, the space was curved and acted like a magnifying glass which bent the light coming from more distant galaxies that were behind the SMACS 0723. As the Universe expanded, this light stretched and turned into infrared light which was caught by JWST’s instruments.
The image was taken by JWST’s Near Infrared Camera and Mid-Infrared Instruments. As it was taken in infrared and, as the light from the furthest galaxies of the Universe has turned mostly to infrared, the image contained the faintest and furthest galaxies the humans have ever seen to date – surpassing the Ultra Deep Field image taken by Hubble.
This image, one of the first of many discoveries by JWST would prove very fruitful to understand the evolution of our Universe. This is the time when the first stars were starting to appear and the galaxies were started to come together. Although, they were not as well structured as modern galaxies. These ancient galaxies would go through a lot of collisions, merging, and distorting before they become well-defined.
2. Discoveries of Jupiter
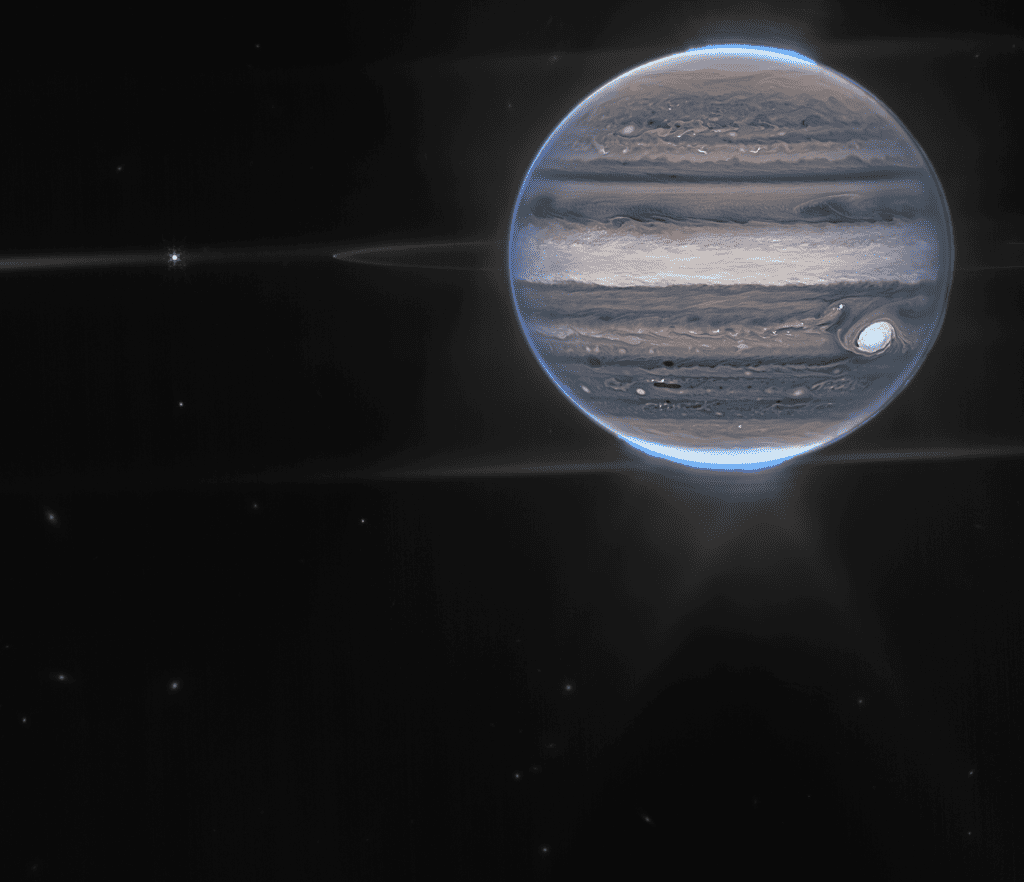
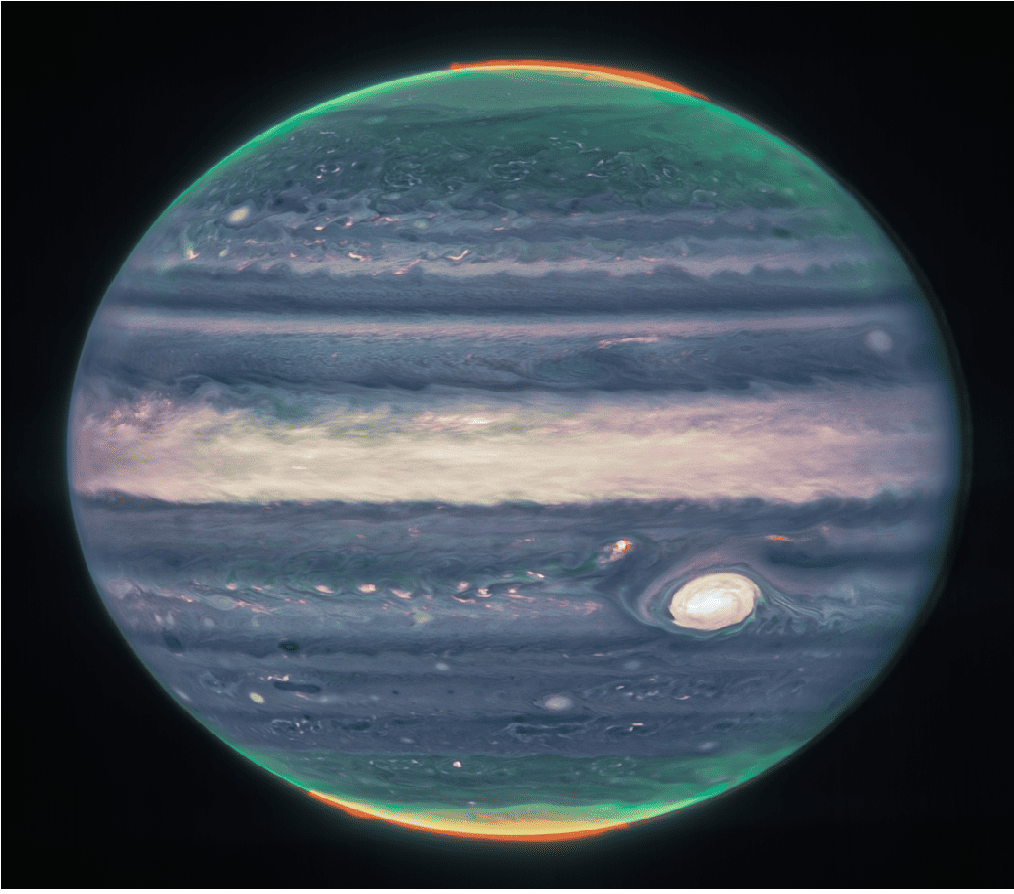

Discoveries by JWST are not only just peering into the Universe, but it also shedding new lights in our Solar System. James Webb has captured some amazing pictures of Jupiter and has made some startling discoveries. JWST’s Near Infrared camera captured Jupiter in three types of filters – Red, Yellow-Green, and Cyan. The resulting image is breathtaking and it has shed new light on many aspects of the gas giant.
Discoveries by JWST about Jupiter could give scientists more insights about its chemical composition, atmosphere, weather pattern, poles, and about its Great Red Spot. JWST’s close-up image shows The Great Red Spot of Jupiter in a new light. It appears bright white as it reflects a lot of Sunlight. The brightness indicates the presence of high-altitude haze.
This can also be seen in the Equatorial region. Before JWST, the Juno mission had also detected this high-altitude haze in a thin band where the stream of swirling gasses collides with each other. But JWST shows the high-altitude haze in an expanded view. The various glaring specks and stripes over Jupiter’s atmosphere indicate the presence of clouds above the swirling gasses.
The auroras in Jupiter’s pole shine in a redder spectrum. The auroras go up in the atmosphere of Jupiter and extend further from the poles. A greenish and swirling fogy cloud can be seen extending from the poles. In wide-angle view, the auroras appear more in the bright blue blaze. The blaze stretches from the poles to high up in the atmosphere. Stream of lights, refracted probably by the auroras or the atmosphere, can be seen extended in the void of space. These discoveries by JWST will allow scientists to study its poles and magnetic field in greater depth.
The wide-angle view of Jupiter also captures the thin ring that surrounds the Jovian Planet. Unlike Saturn’s spectacular rings, this ring is extremely faint and appears as a wafer-thin band circling the Gas Giant. Two of Jupiter’s moons – Amalthea and Adrastea – also appear alongside some very distant galaxies which are faintly illuminated by the very stretched infrared light.
3. Discoveries about Saturn’s Moon Titan
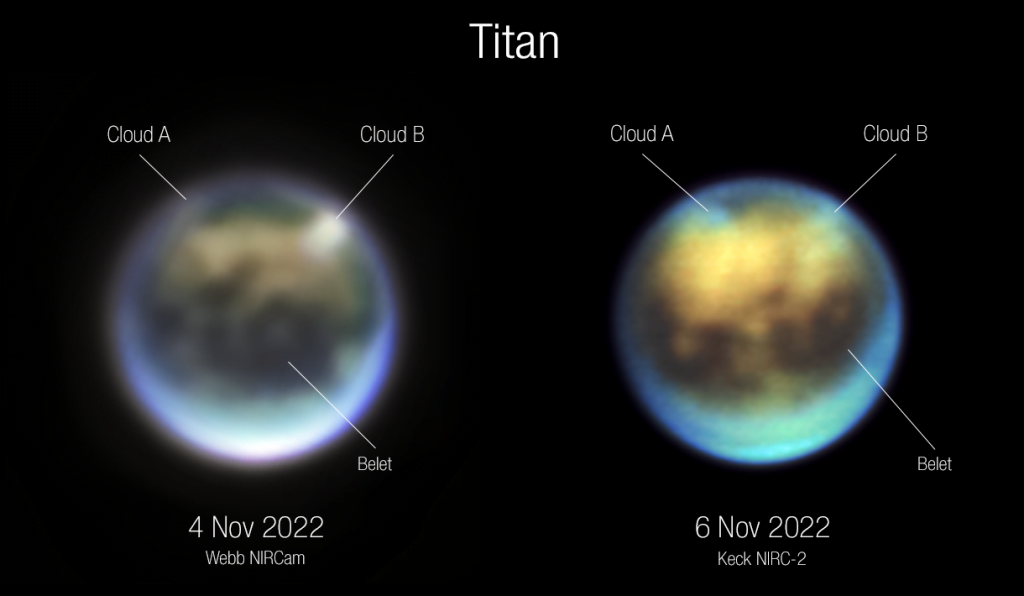

The discoveries by JWST about Saturn’s one of moons, Titan, have fascinated the Scientific community. JWST peered into the atmosphere of Titan – one of Saturn’s Moons. Titan is rare in that it is the only Moon in the Solar System that has a thick atmosphere made of Methane and Nitrogen. Titan has seasons, rain, rivers, lakes, and oceans.
Although it is too cold to have water. Instead, it has liquid hydrocarbon which evaporates in the upper atmosphere and then condenses and falls in the form of rain and flows into the surface creating rivers, lakes, oceans, etc. It is thought that when the Sun becomes a red giant and engulfs the Earth, moons like Titan will warm up and become habitable.
So, the Titan is of great importance to Scientists, and JWST, along with the Keck Telescope had peered through its thick atmosphere to scientists’ delight, the infrared images have confirmed the presence of two sets of clouds, visible as bright spots in the Northern hemisphere of the Saturn’s moon. The clouds were in the same place even after more than 24 hours and by that time they had changed shape.
These discoveries by JWST are of great importance as they confirmed that during the summertime when the Surface receives ample Sunlight, Titan’s atmosphere warms up and creates clouds. The clouds stay at the same spot and change shape, confirming the atmospheric activities on the Moon. These discoveries by JWST and Keck confirmed the ability of Titan’s atmosphere to create clouds in warmer Weather.
Scientists are hopeful to make new discoveries once they analyze the full data collected by JWST. These are good prospects for the ability of Jovian moons to have Earth-like climatic features and to sustain life beyond Earth when the Sun swells up. Perhaps in the future, these moons will be able to sustain the advanced intelligent life remaining in the Solar System after the Sun becomes a Red Giant.
4. Discovering CO2 on An Exoplanet

Discoveries by JWST are creating history. For the first time in human history, we humans are able to peer through the atmosphere of an exoplanet, which is almost 700 light years away from Earth, and discover its element. WASP 39b, an exoplanet orbiting a Sun-like star, will go down in history as the first planet outside our Solar System whose atmospheric composition was discovered by direct observation.
WASP 39b is a Hot Jupiter that circles its host star at very close proximity. The distance between the planet and its host star is only 0.05 AU which is only 1/8 the distance between the Sun and Mercury. The planet is little more than 1/4 the mass of Jupiter. As it orbits its Star at very close proximity, it has an extreme temperature – almost 900 degrees Celsius. It takes only 4 Earth Days for the planet to complete its one orbit around the star – meaning its one year is only 4 days on Earth.
JWST has spied into the atmosphere of WASP 39b and has found concrete evidence of Carbon Dioxide – CO2. While the planet was orbiting the star, JWST observed the light that was coming from it. The light coming from the Star would get absorbed by various elements that exist on the planet. Each element would absorb a specific wavelength of light. CO2 in the atmosphere of the planet has absorbed that specific wavelength of light which was shown as the spike in the spectrum analysis of the light -coming from the WASP 39b.
This is one of the most important discoveries by JWST as the detection of CO2 in an exoplanet’s atmosphere would hint at the presence of life. Of course, for WASP 39b there is no probability of finding life as we know it as its temperature is too high even for simple life and as it is a gas giant, it does not have any solid surface. But, an Earth-like rocky planet, orbiting its Star at Goldilocks zone, would have promising aspects for life and, if JWST could detect the presence of CO2 in its atmosphere, then that would be one step closer to finding life beyond Earth.
5. First Ever Direct Image of An Exoplanet
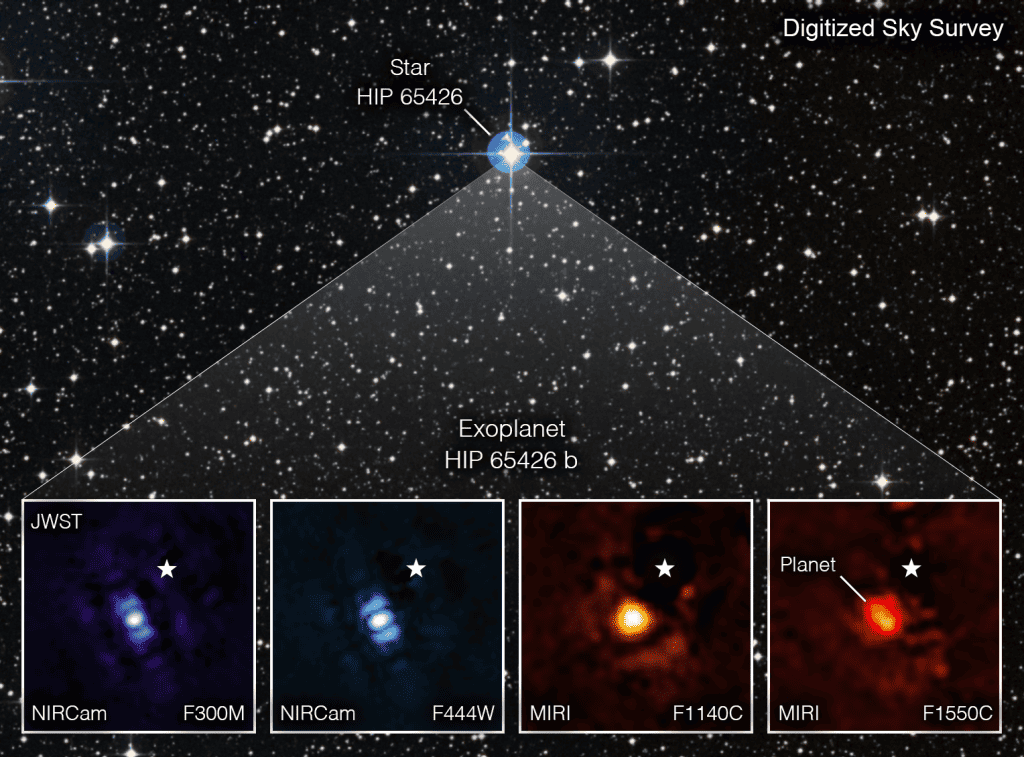
The discoveries by JWST are going to shape the future of mankind. One of those discoveries was the direct image of an exoplanet – HIP 64526 b. The planet orbits the Star named – HIP 64526. The planet is a gas giant and is about 5-10 times the mass of Jupiter. It is a relatively young Star system and the planet is only about 15 Million old.
Imagining an exoplanet far from our Earth is a challenging endeavor. The planets are very small compared to their host Star and they get obscured by the blazing brightness of the host Star. Till now scientists have been using indirect methods to discover exoplanets. However, JWST’s ability to directly image an exoplanet, coupled with its ability to map out the atmosphere of an exoplanet, will change the landscape of planet hunting. These discoveries by JWST are enabling us to find habitable rocky planets outside our Solar System.
The planet – HIP 64526 b – is orbiting its Star at a distance that is 100 times the distance between Earth and the Sun. The planet is also 10,000 times dimmer than the Star, making it extremely hard to image it directly. However, using James Webb’s sensitive infrared cams – NIRCam and MIRI – scientists were able to separate the image of planets from the brightness of the host Star. The instruments of the James Webb have blocked the lights coming from the Star and imaged the planet. While NIRCam has imaged the planet in 3 micrometers and 4.44 micrometers, the MIRI has imaged it in 11.4 and 15.5 micrometers.
6. Discoveries in Pillars of Creation
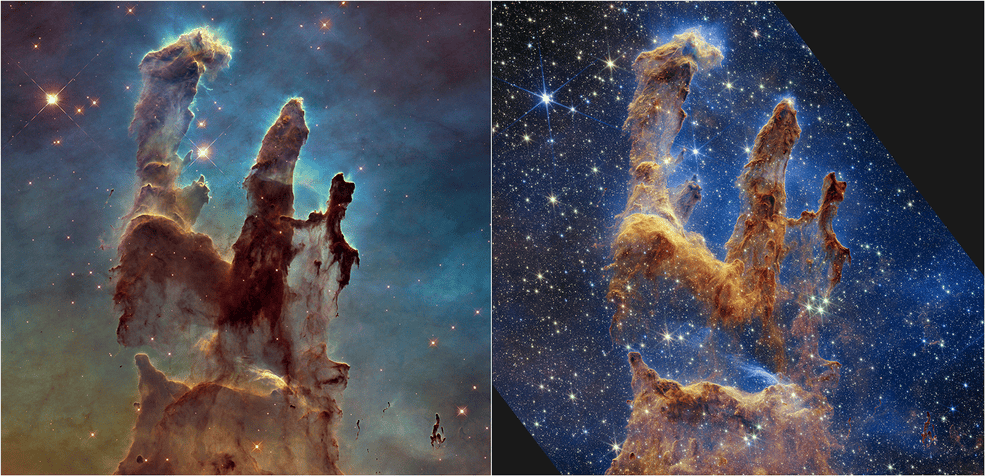
In 1995, the Hubble Telescope gazed at its view of the Eagle Nebula to capture the image of interstellar gas and dust in the constellation of Serpens which is about 7,000 light years away from Earth. The collection of dust and gas looked like huge pillars and was dubbed as ‘Pillars of Creation’. Within these pillars of interstellar gas and dust, new Stars are being born.
In October 2022, JWST looked at these pillars in both NIRCam and MIRI and captured some stunning and ghostly images of these pillars. The NIRCam has taken images in shorter wavelengths (0.6 to 5 microns). These images are much sharper and reveal the Pillars of Creation in all its glory. It shows the birth of new stars as they shine in the bright red infrared spectrum. The images also capture the stellar ejections coming out from these young stars which are only around hundreds thousand years old.
On the other hand, MIRI captures the longer wavelength (5 to 28 microns) of infrared light and reveals a ghostly figure of these pillars. As the newborn stars do not shine in longer wavelengths, they are not being revealed in the images taken by MIRI of JWST. These discoveries by JWST will allow scientists to more accurately calculate the amount of gas and dust present in the pillars.
These discoveries by JWST will enable scientists to figure out the number of Stars that are being born in the nursery. Scientists will also be able to grasp the exact process of Star formation and figure out with precision the amount of time needed for this process. In turn, these discoveries by JWST will allow scientists to better understand the evolution of Star formation, the process of formation of galaxies, and the impact both had on the evolution of the Universe.
7. Ripples of Wolf-Rayet Star
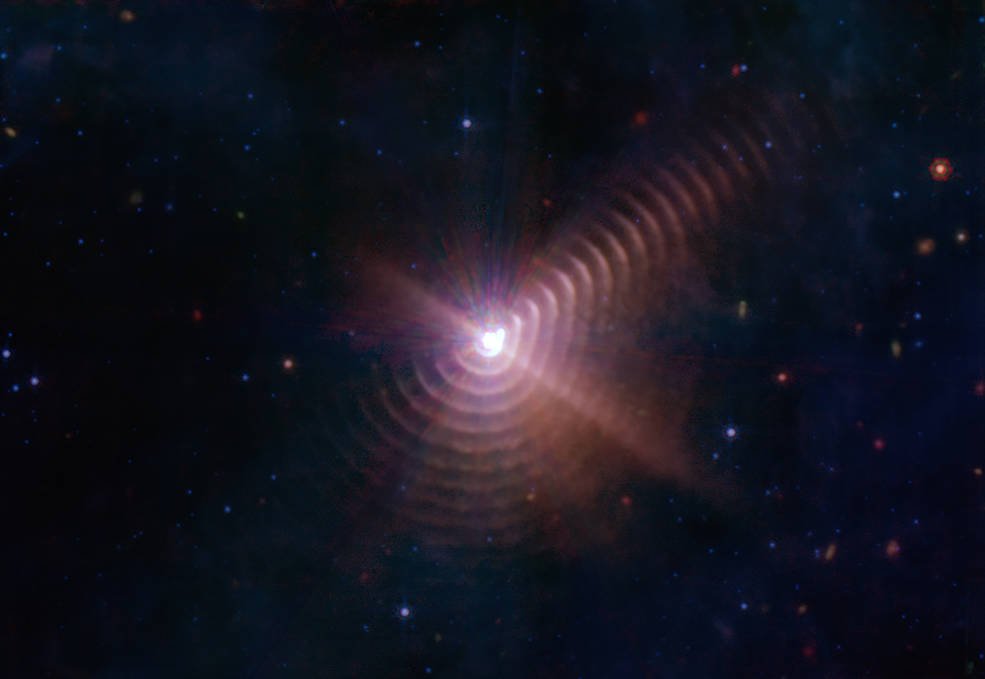

At least 5,000 light years away from Earth exists a binary Star system made of a Wolf-Rayet Star and its smaller companion. The bigger star of the system is called an O-type star which is at least 25 times more massive than or Sun. This star is at the last stage of its life and will be destroyed by the Supernova explosion, creating either a pulsar or a black hole at the end.
Dubbed as Wolf-Rayet 140, the binary system has produced at least 17 dust rings. The bigger O-type star has used up all its Hydrogen and now shedding its inner layer of mass which is made of heavier elements – able to create dusty formations. When both companion, while orbiting each other, comes close, the O-type star would shed its outer layer. The stellar wind from the companion would collide with the dusty materials and due to the gravitation interplay, these stellar gas and dusts would compress and create these rings.
These rings are captured by the MIRI – a camera of JWST. As the materials, that have created these rings are much colder than the stars, the rings emit longer wavelengths of infrared light which MIRI can detect using its sensitive instruments.
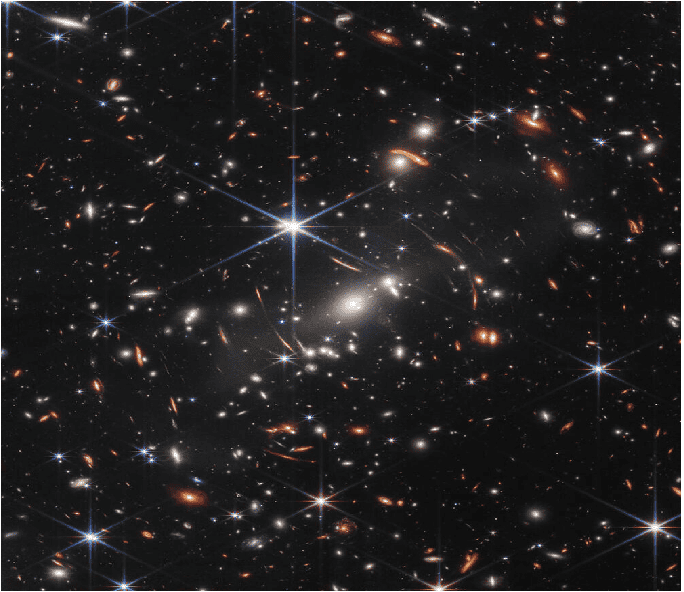
8. Six ‘Universe Shattering’ Distant Galaxies
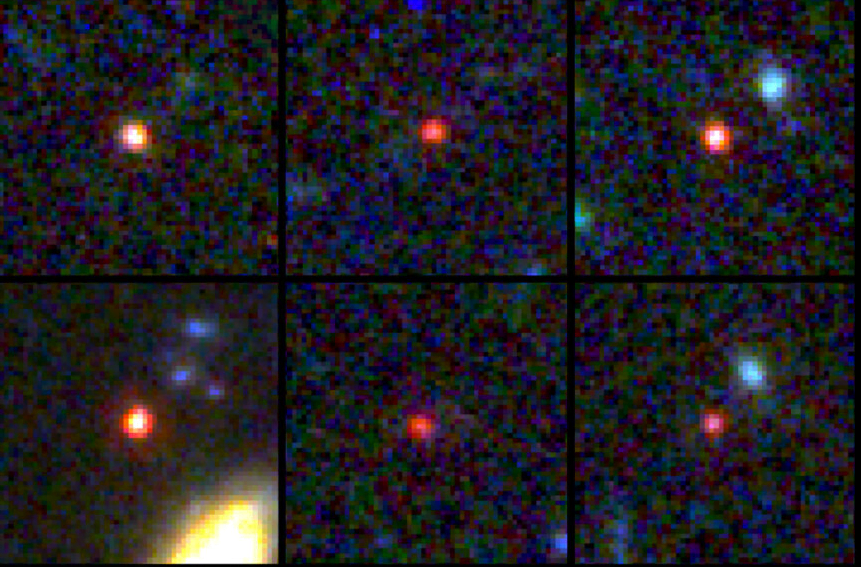

Of all the discoveries by JWST, this one has the potential to shatter our view about the creation of the Universe and the Big Bang. According to the current theories, the Big Bang happened around 13.8 Billion Years ago. After that, it took around 150 to 200 Million years for the first stars to form which are called Population 3 stars. Then around 300 to 400 million years after the Big Bang the galaxies started to form and it is believed that it took at least 1 Billion years after the Big Bang for those galaxies to amass critical size and mass to be deemed as galaxies.
Of course, the process of the evolution of galaxies does not stop there and it continues. However, one of the discoveries by JWST has challenged all these notions. In July 2022, JWST imaged six galaxies (appearing as red dots in the image) which seem to have formed just 500-700 Million years after the Big Bang. This discovery is of great importance as those galaxies seem to be fully grown and evolved galaxies. It seems that these six have a mass of 10 Billion to 100 Billion Suns – an astonishing.
Galaxies did exist at that time but they were small and did not have such huge mass. According to our current understanding, the galaxies which were formed 700 Million years after the Big Bang should be smaller and should be less massive than these six galaxies. For comparison, our Milky Way galaxy formed 13 Billion years after the Big Bang and through various mergers and evolutions, it grew to its current size. The Milky Way currently has a mass of 60 Billion Suns.
Of course, more study of data is needed to establish that these six red dots are actually galaxies and not some other exotic objects. Either way, one of the most astonishing discoveries by JWST has given scientists a chance to better understand the evolution of our Universe.
*Most of the information in this article comes from NASA.
Read More
- Space Science: 6 Vital Reasons Why We Should Invest in It
- Solar System: 10 Astonishing Uniqueness of our star system
- Our Universe: An Incredible Journey of 13.7 Billion Years
- Indian Gooseberry (Amla): 10 Amazing Facts About This Wonder Fruit
- Top 6 Solar System Objects That Might Destroy Life On Earth
- The Great Physicist Peter Higgs Passes Away at 94
- Certain End of The Universe: 4 Forces of Nature to Watch Out For
- Big Bang: An Incredible Start of Universe 14 Billion Years Ago




